Access a range of datasets and data tools to further your research into aeolian landforms.
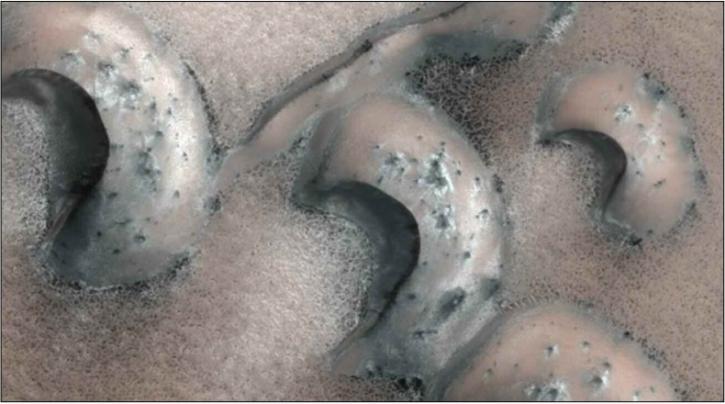
An aeolian landform is a part of the landscape shaped by the wind. Examples of aeolian landforms include sand dunes, snow and ice structures, and areas of wind-eroded stone known as ventifacts. The term “aeolian” comes from Aeolus, the ruler of wind in Greek mythology.
Wind can sweep sediment into formations and carry sand or ice crystals that wear down geological structures. Aeolian landforms are especially common in areas that have few obstacles to block the wind and little vegetation to hold sediment in place, such as deserts. Sometimes, aeolian landforms created by windblown deposits can become more durable if vegetation grows on top of them and secures them with systems of roots, as is common with coastal dunes.
NASA's Earth-observing satellites collect a variety of data useful to the study of aeolian landforms, including land topography measurements and weather observations. These data help researchers understand the changing landscape of our planet and how shifts in the terrain affect ecosystems.
Learn How to Use Aeolian Landforms Data
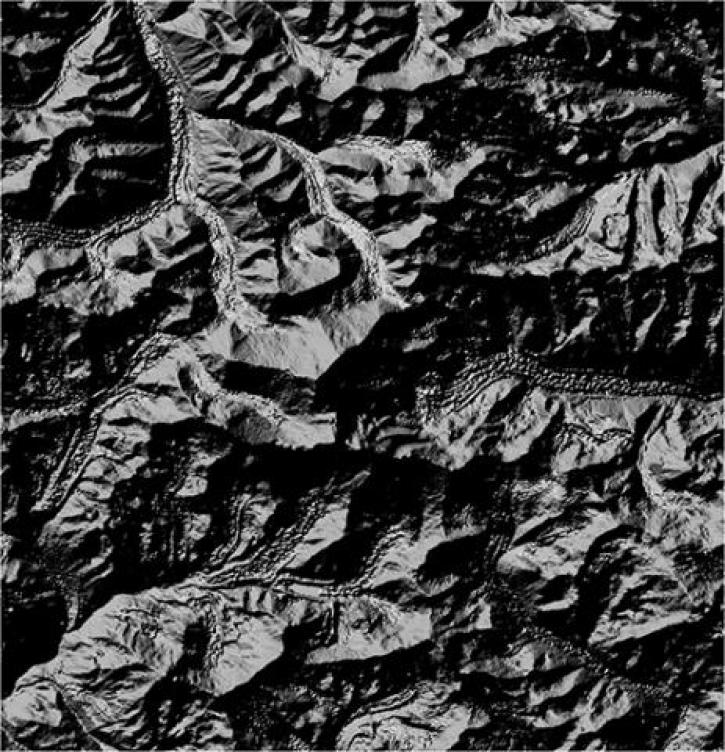
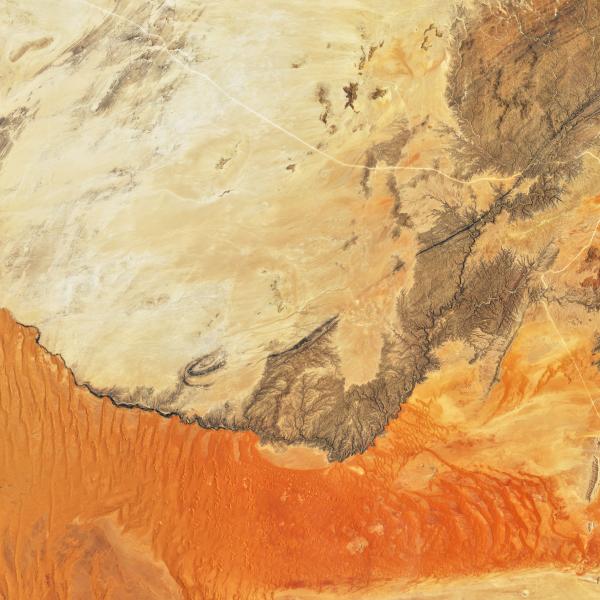


Join Our Community of NASA Data Users
While NASA data are openly available without restriction, an Earthdata Login is required to download data and to use some tools with full functionality.
Learn About the Benefits of Earthdata LoginFrequently Asked Questions
Earthdata Forum
Our online forum provides a space for users to browse thousands of FAQs about research needs, data, and data applications. You can also submit new questions for our experts to answer.
Submit Questions to Earthdata Forumand View Expert Responses