Access a range of datasets and data tools to further your albedo research.
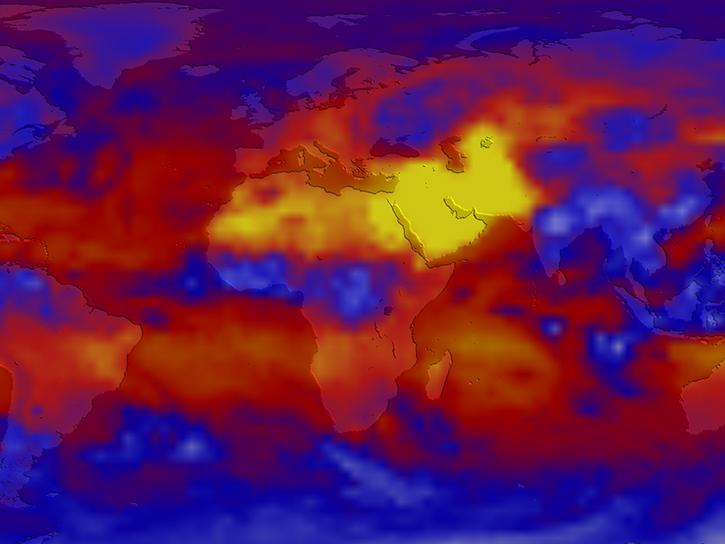
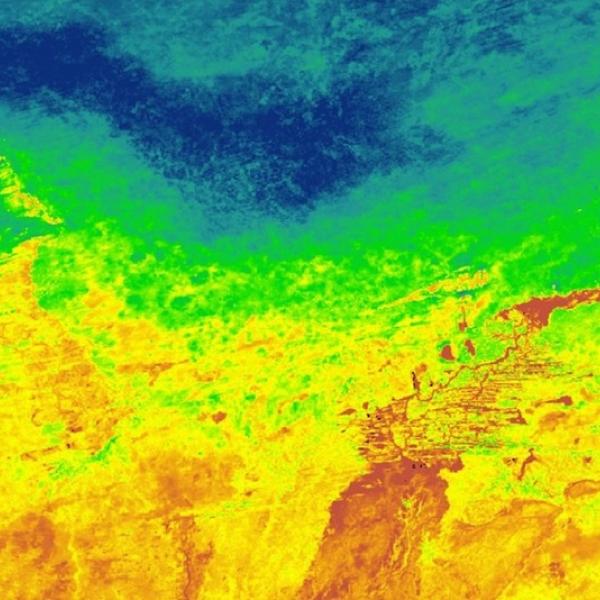
Albedo is a measure of the percentage of sunlight that a surface reflects away. Different parts of Earth’s surface have different albedos. Fresh snow can have an albedo of up to 0.85, meaning that it reflects 85% of the sunlight that hits it. On the other end of the scale, open ocean can have an albedo lower than 0.1, absorbing over 90% of incoming sunlight and reflecting less than 10%.
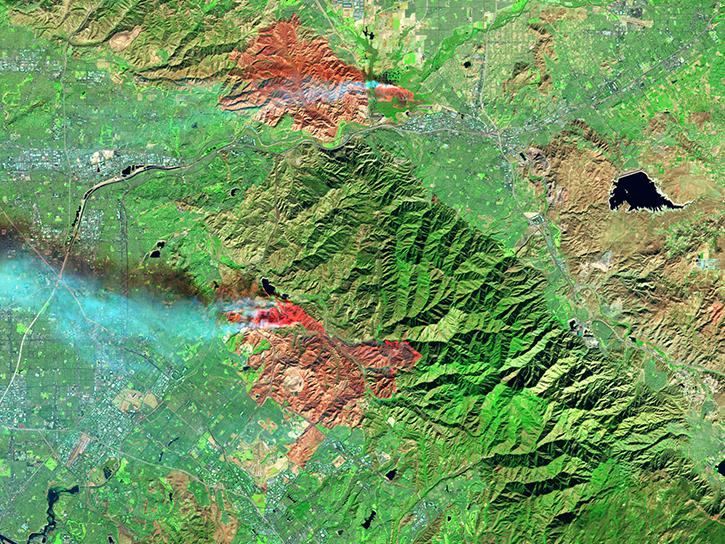
One of Earth’s highest-albedo phenomena are clouds, which reflect high percentages of sunlight back into space. Land surfaces with higher albedos include snow, ice, and deserts, while land surfaces with lower albedos include urban areas and forests. Bodies of water also have low albedos. If the average amount of incoming sunlight equals the average amount of outgoing sunlight, Earth’s temperature remains roughly constant over time; otherwise, Earth’s temperature changes.
NASA’s Earth-observing satellites carry instruments that measure albedo and surface reflectance worldwide. This helps researchers answer crucial questions about how the planet’s temperature is changing over time, the effects of human activity on surface reflectance, and how the Sun’s energy interacts with Earth.
Learn How to Use Albedo Data

Join Our Community of NASA Data Users
While NASA data are openly available without restriction, an Earthdata Login is required to download data and to use some tools with full functionality.
Learn About the Benefits of Earthdata LoginFrequently Asked Questions
Earthdata Forum
Our online forum provides a space for users to browse thousands of FAQs about research needs, data, and data applications. You can also submit new questions for our experts to answer.
Submit Questions to Earthdata Forumand View Expert Responses