If you live in the south and you have never heard of armyworms before, that is likely to change. Armyworms have
become a significant problem for the south, southeast, and northeastern U.S. reaching even into southeastern Canada. Recently, the University of Alabama Extension (UAE) noted a significant outbreak of fall armyworms. These insects, which reproduce quickly, can rapidly consume green vegetation and cause extensive damage to not only agriculture, but also lawns and gardens. In a pest report from July 23, the UAE noted a number of armyworm and related pest species five times greater than last year. In the Huntsville, Alabama area farmers and homeowners are experiencing significant loss to their properties as a result of armyworm infestations.
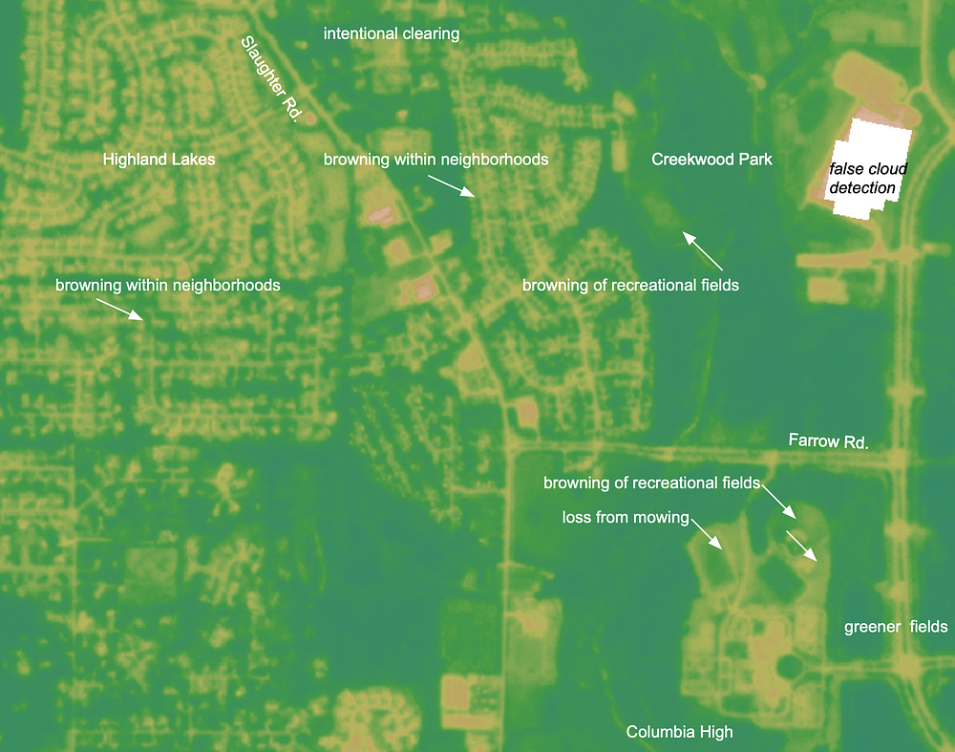
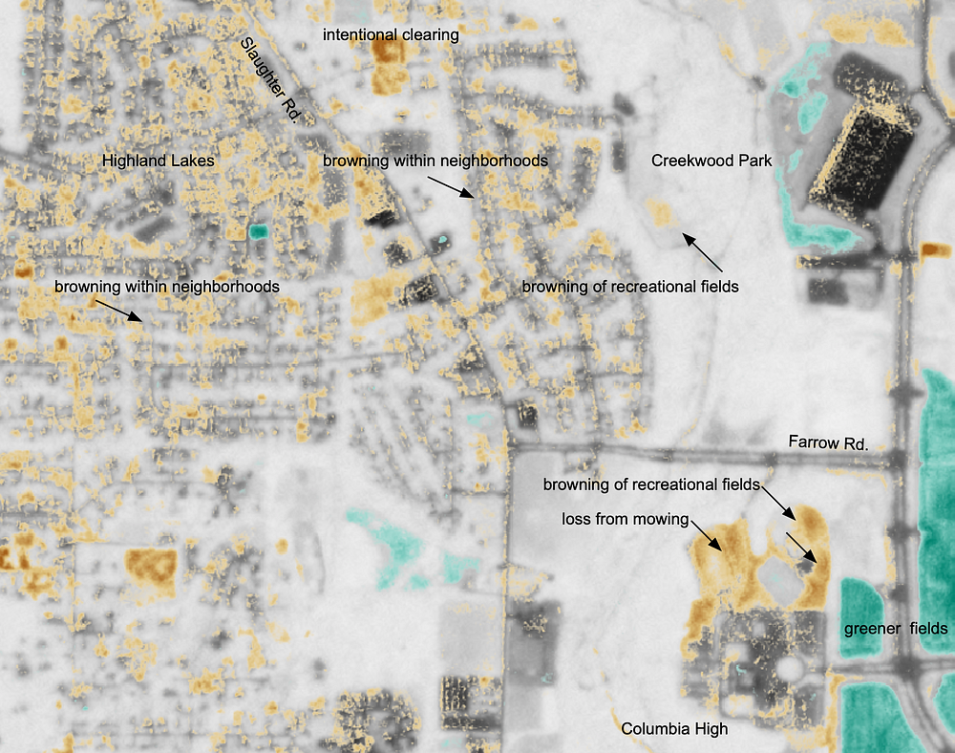
Optical remote sensing can identify rapid changes in vegetation conditions by focusing on the analysis of visible and near-infrared surface reflectance data. For homeowners, one such visible change is the loss of green color to their lawns as the armyworms consume leaf material from the blades of grass, leaving behind barer soils or the drier, less-green stems of vegetation. From a remote sensing perspective, satellites with bands in the red, green, and blue components of the visible spectrum can see some of these effects much in the same way as the human eye. However, they have a unique vantage point with a band in the near-infrared, which humans cannot see, that provides information on the distribution of green vegetation. Therefore, imagery from space may also become less green and change to shades of brown as green vegetation is damaged. Likewise, parameters derived from these sensors with an emphasis on green vegetation, such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), leverage the vantage point of the near-infrared to monitor vegetation conditions. The World Bank has invested in research using remote sensing to help identify armyworm infestations and impacts.
Because lawns and fields are relatively small in scale, higher spatial resolution imagery is helpful in detecting these changes. NASA has partnered with Planet through the Commercial SmallSat Data Acquisition (CSDA) program to make higher spatial resolution imagery available to several federal agency partners interested in mapping the Earth’s surface. Planet operates a large constellation of small satellites observing the Earth in the visible to near-infrared wavelengths, which provides the ability to map vegetation in cloud-free conditions down to the spatial scale of a few meters. This complements global observations by NASA and other partners that monitor vegetation at a coarser spatial scale. NASA and federal partners can use Planet assets to explore how they can detect smaller-scale damage features that may be more difficult to detect from lower resolution sensors.
IMPACT team member Andrew Molthan accessed Planet data available from the CSDA program. He selected relatively cloud-free imagery with good viewing conditions prior to and after the report of armyworm impacts. Scenes were acquired for the local Huntsville area, as well as a few regions of documented impact reported on Twitter, to help determine the quickness and magnitude of change. From these scenes, he generated true color imagery and NDVI products for a purely qualitative look at any changes in the region. Local armyworm presence was confirmed through first-hand observations that included neighborhood observations, local field checks, and media reports. Visual interpretation can be challenging as there are a number of other potential land surface changes going on at the same time. For example, the Huntsville area includes farm fields that are either continuing to grow (green-up) or being harvested; land may be cleared for new construction; residential foliage may be going through seasonal color change; and slight variations in sun angle and changes in building shadows are possible between multiple scenes. With so many changes occurring, it can be difficult to attribute a change to a specific source. The images and short-term comparisons demonstrate how NASA’s partnership with Planet allows analysis of higher resolution imagery that can capture sudden changes that may be of local interest. Similar changes are likely observable in other regions as the autumn armyworm outbreak unfolds across the eastern United States.