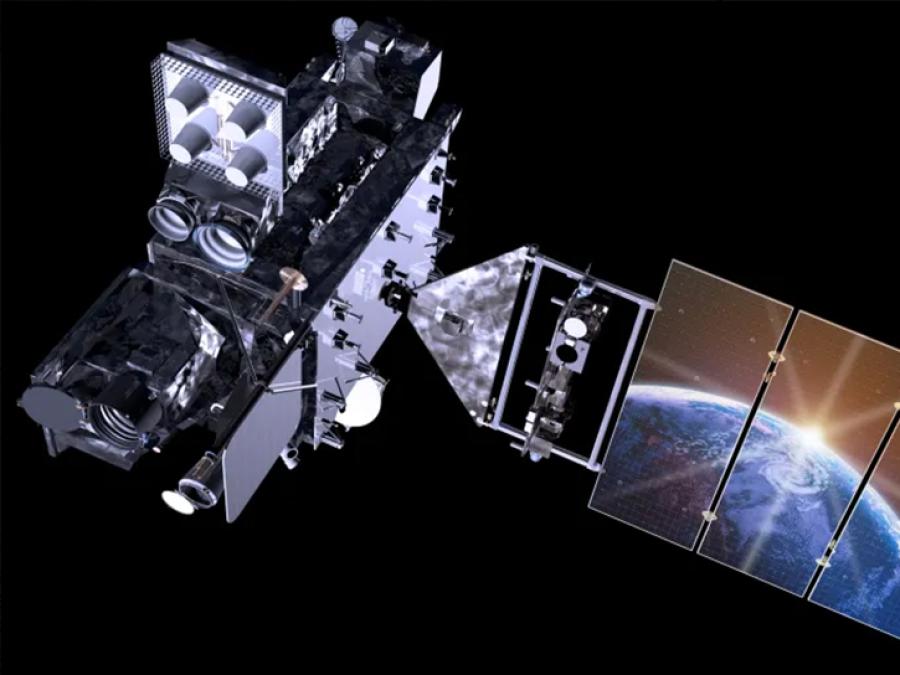
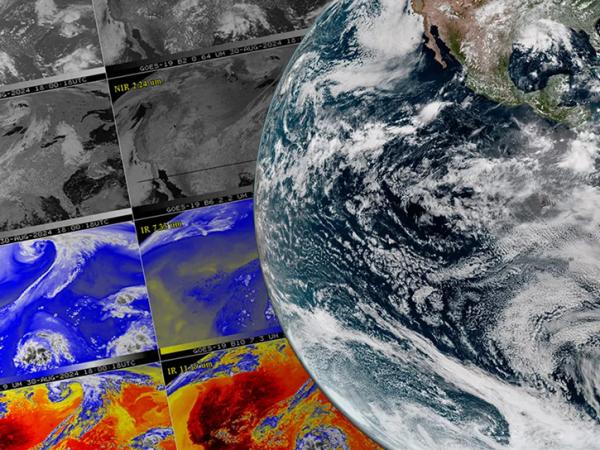
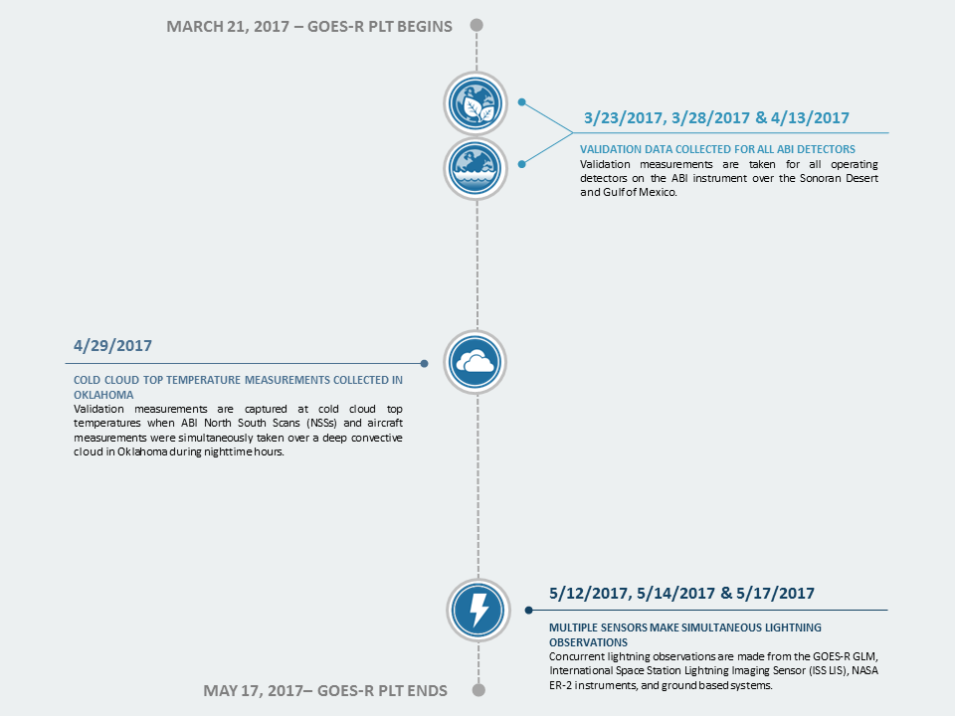
The goal of the GOES-R PLT campaign was to provide a collection of coincident airborne, satellite, ground based, and near surface measurements of surface weather phenomena to test, validate, and improve the accuracy of GOES-R ABI and GLM measurements.
The campaign was comprised of two phases: the first centered on the U.S. west coast, providing tests primarily for the ABI instrument, and the second focused on the central and eastern U.S. with tests primarily for the GLM instrument. Airborne measurements were taken using NASA’s ER-2 aircraft, equipped with spectrometer, radar, lidar, radiometer, and other atmospheric observation instruments to assist with ABI and GLM validation. The target phenomena for validation observations included land and ocean surfaces, active wildfires, and thunderstorms. This campaign provided a blueprint for the operation of future GOES validation projects.
The primary objectives of GOES-R PLT field campaign included:
- Provide high altitude validation of spectral radiance measurements for all ABI spectral bands
- Provide surface and atmospheric geophysical measurements for validation products
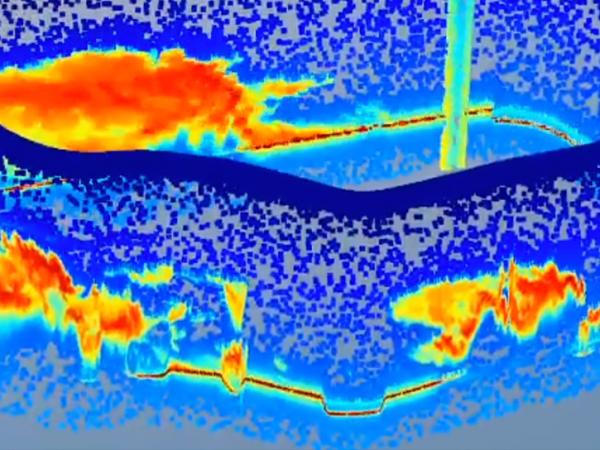
- Validate GLM lightning flash detection efficiency over land and ocean
- Validate the location and time accuracy of GLM flash detection