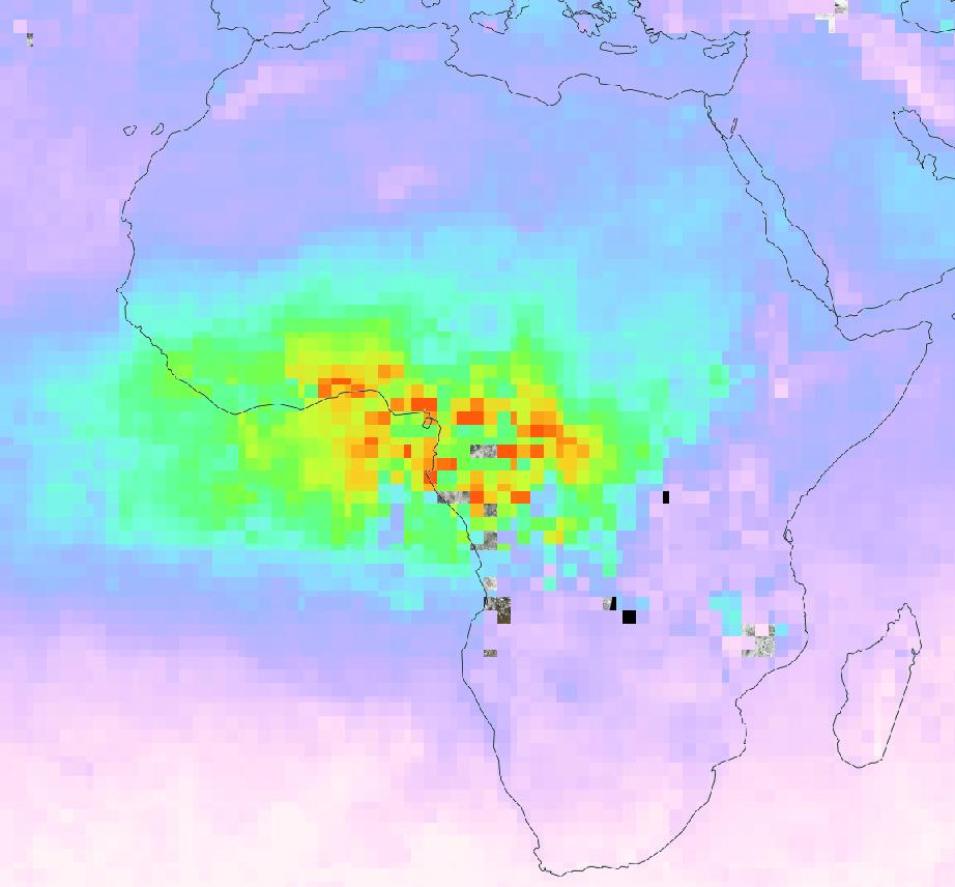
The Measurement of Pollution in the Troposphere (MOPITT) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite is designed to enhance our knowledge of the lower atmosphere and to observe how it interacts with the land and ocean biospheres. MOPITT’s specific focus is on the distribution, transport, sources, and sinks of carbon monoxide in the troposphere.
MOPITT is one of the earliest satellite sensors to use gas correlation spectroscopy. The sensor measures emitted and reflected radiance from Earth in three spectral bands. As this light enters the sensor, it passes along two different paths through onboard containers of carbon monoxide. The different paths absorb different amounts of energy, leading to small differences in the resulting signals that correlate with the presence of these gases in the atmosphere.