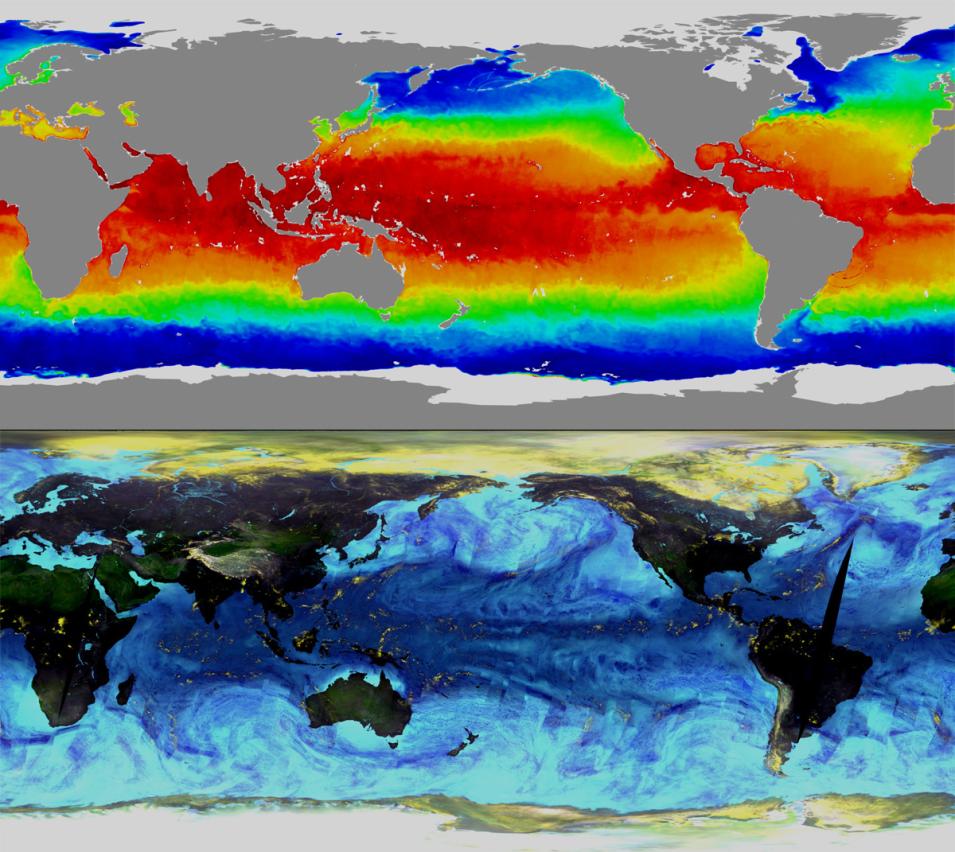
The Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for EOS (AMSR-E) is a 12-channel, six-frequency passive-microwave radiometer aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite designed to study Earth’s water cycle and precipitation rate, cloud water, water vapor, sea surface winds, sea surface temperature, ice, snow, and soil moisture. AMSR-E data are used for investigating how water changes form and location, whether falling as rain or snow, evaporating from the ocean, or freezing on the sea surface, and help scientists better understand the seasonal evolution of sea ice. AMSR-E is a modified version of the AMSR sensor that flew aboard the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Advanced Earth Observing Satellite-II (ADEOS-II). JAXA provided the instrument for the Aqua satellite.
5.4 km at 89.0 GHz to 74 × 43 km at 6.9 GHz
6 bands: 6.9 to 89 GHz with 0.3 to 1.1 K radiometric sensitivity
1-2 days