Satellites can be used to detect all types of fires and other sources of thermal anomalies. This includes thermal activity resulting from burning vegetation (for example, wildland fires or agricultural burning) as well as energy emitted from other, relatively isolated sources of combustion that emit thermal energy. The latter can include other types of natural heat sources (volcanic and other geothermal activity) as well as multiple types of industrial heat sources (including mineral processing plants, gas flares, waste incinerators, cement plants, steel plants, and petrochemical plants). Discerning this type of thermal activity in satellite active fire detection data requires additional information and analysis capabilities.
Enhancing the FIRMS Fire Map Viewer
NASA’s Fire Information for Resource Management System (FIRMS) team has developed and integrated additional data layers and new capabilities within the FIRMS Fire Map viewer to identify active fire detections not associated with vegetation fires. One of these layers is the Static Thermal Anomalies (STA) - Mask layer. This layer is derived using the cumulative active fire detections data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Terra and Aqua platforms as well as the 375m S-NPP VIIRS active fire detection data for calendar year 2023.
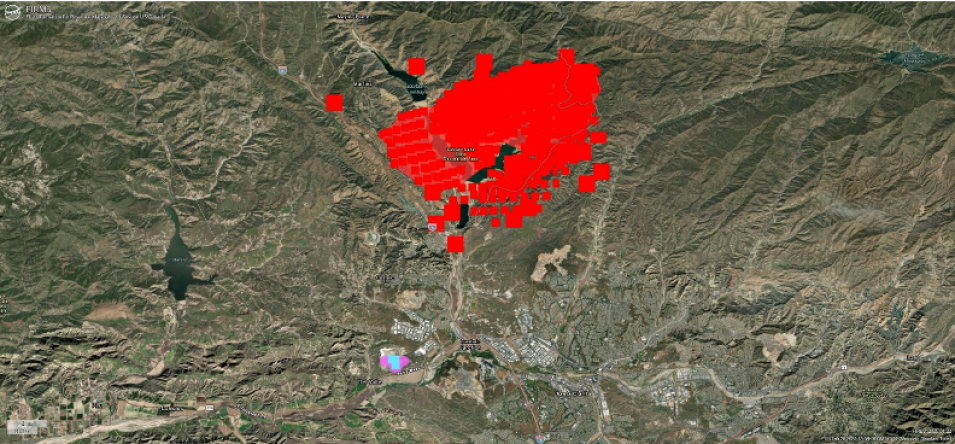
The centroids of the active fire detections are summarized on a 400m grid, and any grid cell containing 5 or more active fire detections over the course of 2023 is extracted and the centroid of the grid cell buffered to approximate a 375m pixel size and smoothed to create a mask of frequently observed or static thermal activity. This mask is then filtered using multiple sources of data obtained from authoritative sources that inventory the locations of industrial heat sources and other natural heat sources not associated with the combustion of vegetation.
The final output layer, the Static Thermal Anomalies - Mask, represents a provisional data layer with polygon features defining the approximate geographic extent of thermal activity, detected on a semi-persistent to persistent basis during the calendar year, that are associated with documented industrial heat sources or natural heat sources not related to vegetation fires.
Combining Data Sources to Pinpoint Active Fires
To assist users in identifying detected fires or other thermal activity not associated with the controlled or uncontrolled burning of vegetation, the FIRMS team dynamically analyzes all sources of polar-orbiting active fire detection data—including MODIS, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), and the Operational Land Imager (OLI) aboard Landsat 8—with the Static Thermal Anomalies – Mask to tag detected activity that is likely associated with industrial heat sources or other types of natural heat sources. These dynamically identified detections are represented in the Static Thermal Anomalies - Detections layer and represent probable fires or other heat sources not associated with vegetation fires for the current date range displayed in the FIRMS Fire Map that has been defined by the user.