NASA's Earth Science Division (ESD) established the Commercial Satellite Data Acquisition (CSDA) program to explore the potential of commercial satellite data in advancing the agency's Earth science research and application objectives. The program aims to identify, assess, and acquire data from commercial providers, which may offer a cost-effective means of supplementing Earth observations collected by NASA, other U.S. Government agencies, and international collaborators.
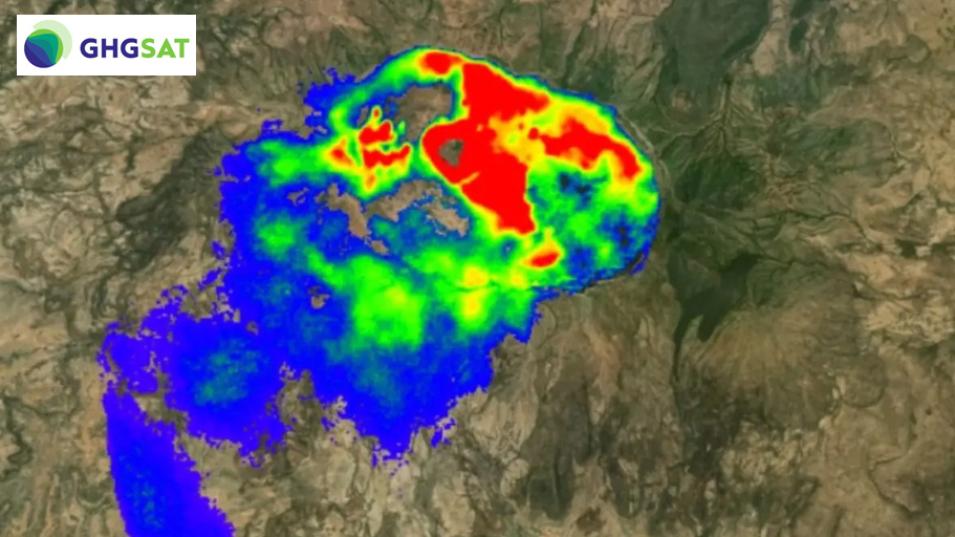
During this NASA CSDA program vendor webinar, speakers will introduce the GHGSat satellite constellation and take a technical deep dive into the methane emission data products. GHGSat scientists will show participants how to access and work with these products, and discuss which research topics the data is best suited for as a point source monitoring system. Additional topics will focus on the services available to data users and getting assistance with GHGSat's datasets, services, and tools.