Science Objectives
In the past, MODIS Vegetation Indices data have been used to study hurricanes after individual hurricane events. It is believed that as sea surface temperatures continue to rise, the potential for more intense and destructive hurricanes with longer lifetimes will also increase. With land temperature increases occurring as well, the rate of drying is also expected to increase. This could cause more intense droughts in a shorter time period, as seen in the Caribbean region.
Instruments Used
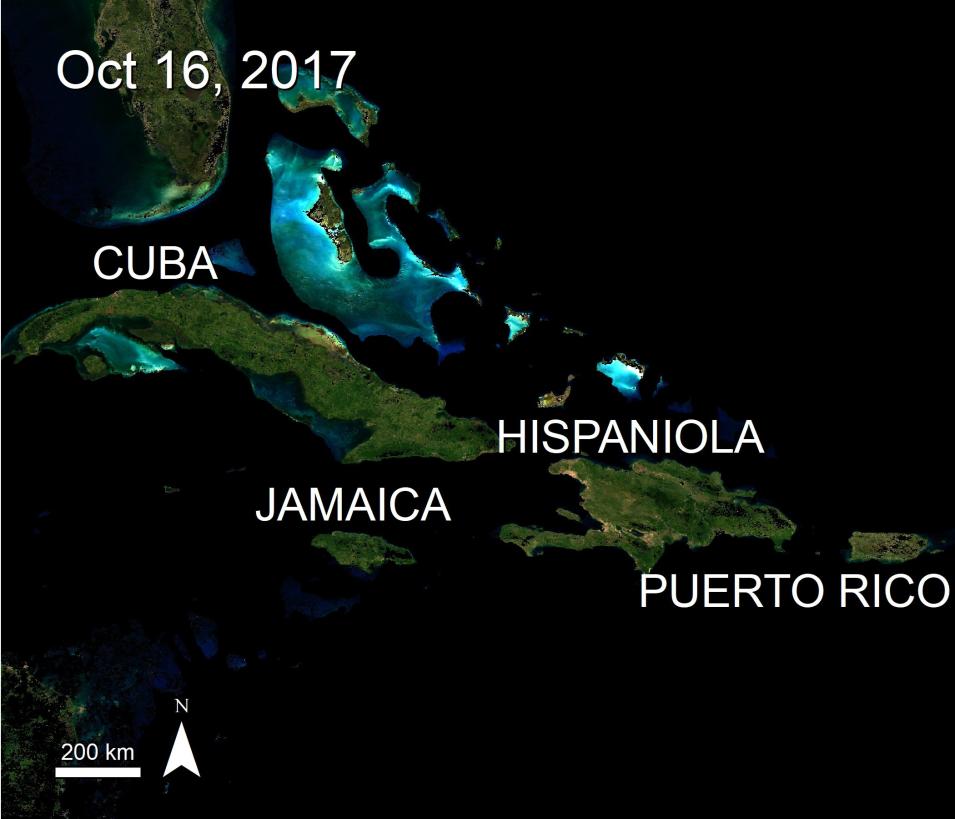
Originally De Beurs and others (2016) created a MODIS-derived disturbance index (DI) based on standardized tasseled cap brightness, greenness, and wetness data. The authors found that the MODIS record, 2000 to present, offers a sufficiently long time series to provide a standardized comparison for their DI. In the paper the authors use MODIS Nadir Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF)-Adjusted Reflectance (NBAR) (MCD43A4) data from 2000 to 2017 to study the impacts of hurricanes and droughts on the four largest Caribbean islands: Cuba, Hispaniola (location of Haiti and the Dominican Republic), Puerto Rico, and Jamaica.
Major Findings
The authors calculate MODIS tasseled cap metrics and generate a disturbance index. Higher DI values (3 or above) suggest significant disturbance. Disturbed land varied between 0 and 50%, with the highest percentages corresponding to major droughts in Cuba and damage from Hurricane Maria in Puerto Rico. For example, Hurricane Maria caused significant disturbance across 50% of Puerto Rico. DI values on vegetated land rose to 3.37, and recovery did not begin until 2.5 months after landfall. The authors believe their approach enables a better understanding of the combined effects of hurricanes and droughts across island landscapes.
References
Publication Reference
De Beurs, K.M., McThompson, N.S., Owsley, B.C., and Henebry, G.M., 2019, Hurricane damage detection on four major Caribbean islands: Remote Sensing of Environment, v. 229, p. 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2019.04.028
Image References
Granule IDs
- MCD43A4.A2017289.h10v06.006.2017298032935
- MCD43A4.A2017289.h10v07.006.2017298031241
- MCD43A4.A2017289.h11v06.006.2017298032929
- MCD43A4.A2017289.h11v07.006.2017298031228
Data Citation
Schaaf, C., and Wang, Z., 2015, MCD43A4 MODIS/Terra+Aqua BRDF/Albedo Nadir BRDF Adjusted Ref Daily L3 Global - 500m V006: NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC, accessed 2019-09-24, at doi:10.5067/MODIS/MCD43A4.006.
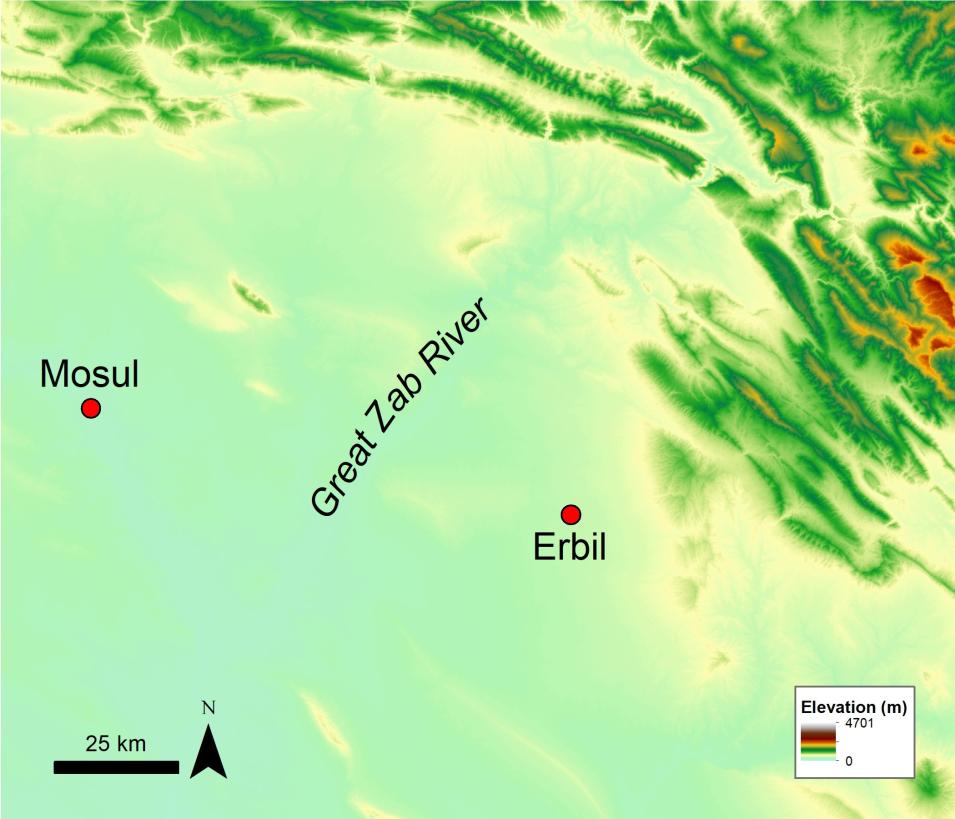
Dam Site Planning in Northern Iraq
In the study "Dam site suitability assessment at the Greater Zab River in northern Iraq using remote sensing data and GIS" published in the Journal of Hydrology, Noori and others (2019) use Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument elevation data and Fuzzy Logic modeling to assess dam construction suitability along Iraq's Greater Zab River.