| AMMR | Calibrated TB (18-37 GHz) | Water vapor profiles (requires temperature profiles) | |
| ARMAR | In-field: Equiv. reflectivity factor Ze, Doppler velocity, Cross-polarization reflectivity,
HH-VV correlation coefficient,
HH-VV phase difference | Rain rate,
Updraft velocity,
Latent heating | Rain rate,
Updraft velocity,
Latent heating |
| AVAPS | Profiles of temperature, pressure, humidity, and wind velocity | | |
| CAPAC | In situ particle density, size, and shape (few um to 1.6 mm for 1st and 4th instrument; 0.2 um to 20 um for 2nd and 3rd instrument).
In-field: above for a few periods | Cloud/aerosol part. size distrib. (0.2 um<D<1.6mm, Diameter);
Condensed water volume | |
| JPL SAW | In situ dewpoint/frostpoint, pressure, temperature (raw data).
In-field: plots of dewpoint/frostpoint | In situ dewpoint/frostpoint, pressure, temperature (formatted data) | |
| Laser Hygrometer | In-situ water vapor volume mixing ratio along the DC-8 flight track | | intercomparisons with the other water vapor sensors on the DC-8; water vapor data will be utilized by the lidar teams and the modelling teams to define atmospheric conditions and analyze atmospheric dynamics |
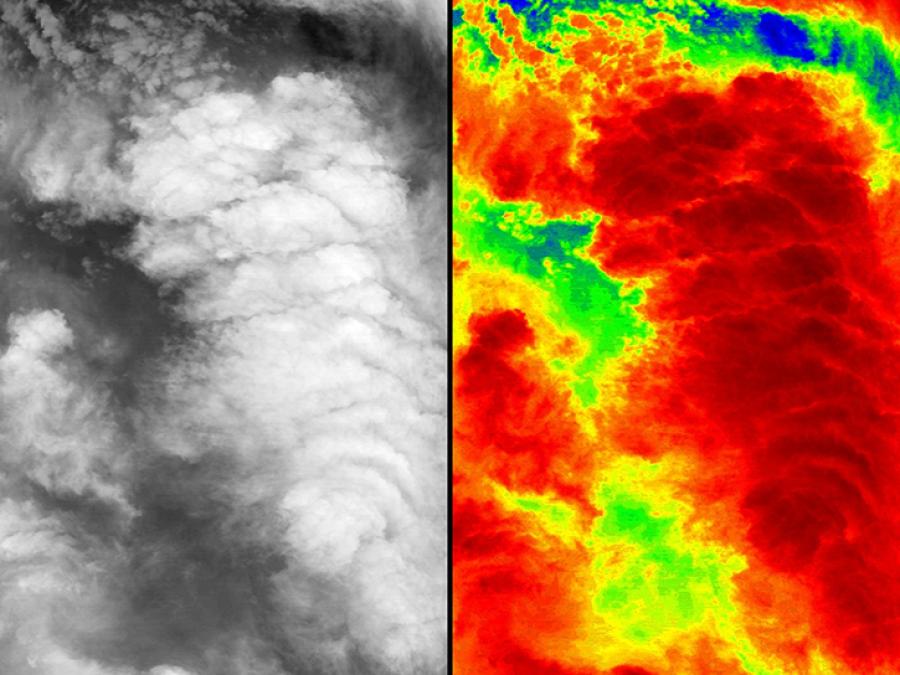
| LASE | Profiles of water vapor mixing ratio and aerosol scattering.
In-field: Color images of water vapor mixing ratio & relative aerosol scatttering cross sections | Cross sections of water vapor mixing ratios, relative humidities, total atmosphere scattering ratios, and aerosol backscattering coefficients | Total precipitation water; Aerosol extinct. profiles; Aerosol optical thickness; Cloud base/top height; Relative humidity profiles; Boundary layer height |
| LIP | Electric field components, aircraft charge.
In-field: Quick looks at direct products | Total lightning count & rates, lightning statistics, storm current output, storm charge structure (last two in conjunction with ER-2 measurements) | Quantified Lightning; relationship with precipitation; convective mass/ice; flux, latent heat; storm current output |
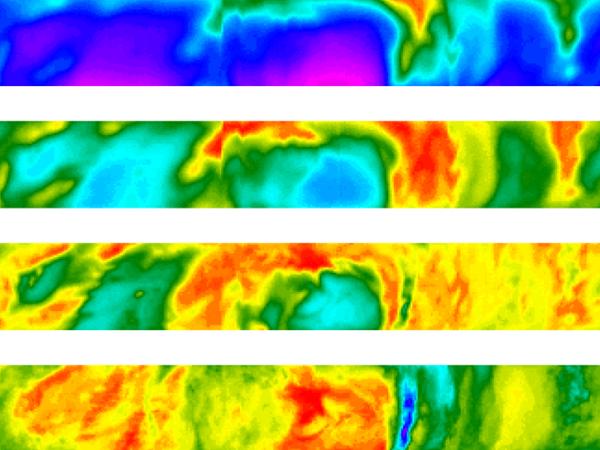
| MACAWS | LOS wind velocities and relative backscatter as a function of location, range from aircraft, elevation angle, & azimuth angle.
In-field: LOS velocity and relative backscatter with respect to time/height | Selected 2-D wind fields as a function of elevation angle with respect to aircraft | 2D wind fields, kinematic quantities, fluxes, Richardson number |
| MMS | 1-Hz data: time, pressure, temperature, theta horizontal wind (U,V), vertical wind (W), turbulence index
5-sec data: latitude, longitude, pressure-altitude, true-air-speed | | |
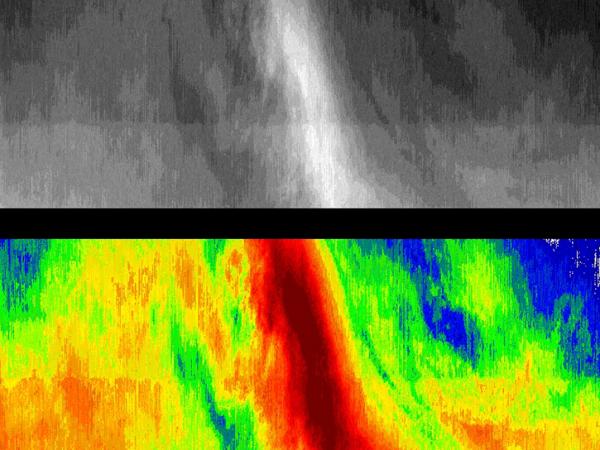
| PSR | Polarimetric, multiband, fore/aft conically scanned, and geolocated brightness temperature maps | Surface wind speed and wind direction, integrated cloud water content, near surface rain rate. | Improved P.I. derived products using rain radar data and integrated water vapor data. |