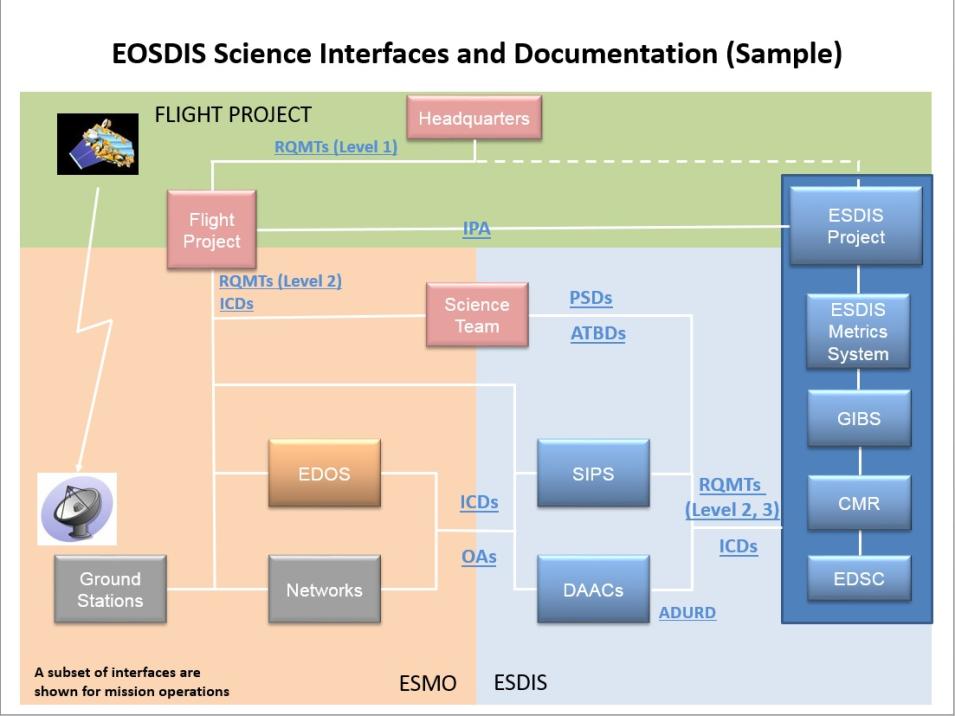
| W/A | Working Agreement | A W/A outlines the working commitments made between ESDIS and another organization for developing, implementing and/or operating portions of the data system. |
| -- | Project Plan | The Project Plan contains the technical approaches and management plans to implement the project requirements. It defines, at a high level, the scope of the project, the implementation approach, the environment within which the project operates, and the baseline commitments of the program and project. (from NPR 7120.5D) |
| DMR | Detailed Mission Requirements | DMRs include Mission-Specific Requirements Documents (MSRDs) and mission requirement documents (e.g., Ground System Requirements Documents [GSRDs], and Mission Operations Requirements Documents [MORDs]). DMRs contain the results of the requirements identification and derivation activities and provide the basis for system design for individual missions. |
| ATBD | Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document | An ATBD describes the physical and mathematical description of the algorithms to be used in the generation of data products. It includes a description of variance and uncertainty estimates and considerations of calibration and validation, exception control, and diagnostics. In some cases, internal and external data product flows are required. |
| ADURD | Archiving, Distribution and User Services Requirements Document | ADURD provides generic requirements for data archiving, data distribution and user services for EOSDIS-supported data. These services are currently being provided by the Distributed Active Archive Centers (DAACs), even though some of the Science Investigator-led Processing Systems (SIPS) are providing these services to a limited extent. |
| ASM | Acquisition Strategy Meeting | An ASM is a forum where senior Agency management reviews major acquisitions in programs and projects before authorizing significant budget expenditures. The ASM is held at the Mission Directorate/Mission Support Office level, implementing the decisions that flow out of the earlier Agency acquisition strategy planning. The ASM is typically held early in Formulation, but the timing is determined by the Mission Directorate. The ASM focuses on considerations such as impacting the Agency workforce, maintaining core capabilities and make-or-buy planning, and supporting Center assignments and potential partners. |
| CDR | Critical Design Reviews | CDRs evaluate the integrity of the program integrated design, including its projects and ground systems. CDRs also help meet mission requirements with appropriate margins and acceptable risk within cost and schedule constraints. CDRs also determine if the integrated design is appropriately mature to continue with the final design and fabrication phase. |
| CERR | Critical Events Readiness Reviews | CERRs evaluate the readiness of the program and its projects to execute a critical event during the flight operations phase of the life cycle. |
| DFCD | Data Format Control Documents | DFCDs and other data format documents (e.g., Data Format Requirements Documents (DFRDs)), define the formats of data units that are transferred across an interface and the control codes used in the data formats. |
| DR | Decommissioning Review | DRs evaluate the readiness of the program and its projects to conduct closeout activities, including final delivery of all remaining program/project deliverables and safe decommissioning/disposal of space flight systems and other program/project assets. |
| DRR | Disposal Readiness Review | DRRs evaluate the readiness of the project and the flight system for execution of the spacecraft disposal event. |
| EOSDIS | Earth Observation System Data and Information System | NASA's Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS) is a key core capability in NASA’s Earth Science Data Systems (ESDS) Program. It provides end-to-end capabilities for managing Earth observation data from various sources – satellites, aircraft, field measurements, and various other programs. For the EOS satellite missions, EOSDIS provides capabilities for command and control, scheduling, data capture and initial (Level 0) processing. These capabilities, constituting the EOSDIS Mission Operations, are managed by NASA's Earth Science Mission Operations (ESMO) Project. NASA network capabilities transport the data to the science operations facilities. The remaining capabilities of EOSDIS constitute the EOSDIS Science Operations, which are managed by NASA's Earth Science Data and Information System (ESDIS) Project. These capabilities include: generation of higher level (Level 1-4) science data products for EOS missions; archiving and distribution of data products from EOS and other satellite missions, as well as aircraft and field measurement campaigns. The EOSDIS science operations are performed within a distributed system of many interconnected nodes (SIPS) and distributed, discipline-specific, Earth science DAACs with specific responsibilities for production, archiving, and distribution of Earth science data products. The distributed data centers serve a large and diverse user community (as indicated by EOSDIS performance metrics) by providing capabilities to search and access science data products and specialized services. |
| ESDIS | Earth Science Data and Information Systems | The Earth Science Data and Information System (ESDIS) Project is a part of NASA's Earth Science Projects Division under the Flight Projects Directorate at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The ESDIS Project manages the science systems of EOSDIS. |
| ESMO | Earth Science Mission Operations | ESMO is responsible for spacecraft maintenance and operations for Earth Science missions conducted by the Earth Science Projects Division at Goddard. ESMO plays a significant role during the mission life cycle; from the formulation and approval phases through the implementation and evaluation phases, and eventual deactivation. The Project's role is to ensure the health and safety of the missions it manages by fulfilling the primary operational requirements for each mission, and providing the scientific community with high-quality data products in a timely manner. It also serves as a focal point for the mission on-orbit operations and the definition of support services required. |
| FA | Formulation Agreement | The FA is prepared by the project to establish the technical and acquisition work that needs to be conducted during Formulation and defines the schedule and funding requirements during Phase A and Phase B for that work. |
| FAD | Formulation Authorization Document | The FAD is issued by the MDAA to authorize the formulation of a program whose goals will fulfill part of the Agency's Strategic Plan and Mission Directorate strategies and establish the expectations and constraints for activity in the Formulation Phase. In addition, a FAD or equivalent is used to authorize the formulation of a project. (See Appendix E.) |
| FRR | Flight Readiness Review | FRRs evaluate the readiness of the program and its projects, ground systems, personnel, and procedures for a safe and successful launch and flight/mission. |
| ICD | Interface Control Document | ICDs are used to record design agreements for the interfaces between participating organizations. ICDs provide a means to evaluate and control all mutually interdependent and/or interacting design parameters of the interface |
| IPA | Inter-Project Agreement | IPAs are agreements between ESDIS and projects not managed by ESDIS. Generally, the projects involved agree on an exchange of support services and data. From the interface control viewpoint, these agreements identify the need for an interface and the scope of the interface. |
| IRD | Interface Requirements Document | IRDs define the requirements for data exchanges across an interface between separately managed systems or subsystems. The requirements statements in IRDs are derived directly from project requirements documents. |
| KDP | Key Decision Point | A KDP is the event at which the Decision Authority determines the readiness of a program/project to progress to the next phase of the life cycle (or to the next KDP). |
| LRR | Launch Readiness Review | LRRs evaluate a program/project and its ground, hardware, and software systems for readiness for launch. |
| LV | Launch Vehicle | LVs are rockets that send people or things into space. |
| MCR | Mission Concept Reviews | MCRs evaluate the feasibility of the proposed mission concept(s) and its fulfillment of the program's needs and objectives. MCRs also determine whether the maturity of the concept and associated planning are sufficient to begin Phase A. |
| MDR | Mission Definition Reviews | MDRs evaluate the credibility and responsiveness of the proposed mission/system architecture to the program requirements and constraints, including available resources. MDRs also determine whether the maturity of the project's mission/system definition and associated plans are sufficient to begin Phase B. |
| MRR | Mission Readiness Reviews | MRRs evaluate the readiness of the program and its projects, ground systems, personnel, and procedures for a safe and successful launch and flight/mission. |
| MRTP | Mission Readiness Test Plans | MRTPs document the strategy that will be used to verify and ensure that all system components working together meet design specifications and requirements for the mission. |
| OA | Operations Agreements | OAs are even lower level, more detailed interface documents that are created to help define the operations use of the interfaces, including such things as addresses, phone numbers, and names of responsible personnel. These documents are not intended for project-level development and control. |
| ORR | Operational Readiness Reviews | ORRs evaluate the readiness of the program, including its projects, ground systems, personnel, procedures, and user documentation. ORRs also operate the flight system and associated ground systems in compliance with program requirements and constraints during the operations phase. |
| PDR | Preliminary Design Reviews | PDRs evaluate the completeness/consistency of the program's preliminary design, including its projects, in meeting all requirements with appropriate margins, acceptable risk, and within cost and schedule constraints, and to determine the program's readiness to proceed with the detailed design phase of the program. |
| PFAR | Post-Flight Assessment Reviews | PFARs evaluate how well mission objectives were met during a human space flight mission. PFARs also evaluate the status of the flight and ground systems, including the identification of any anomalies and their resolution. |
| PLAR | Post-Launch Assessment Reviews | PLARs evaluate the in-flight performance of the program and its projects. PLARs also determine the program's readiness to begin the operations phase of the life cycle and transfer responsibility to the operations organization. |
| PRR | Production Readiness Reviews | PRRs evaluate the readiness of system developer(s) to produce the required number of systems within defined project constraints for projects developing multiple similar flight or ground support systems. PRRs also evaluate the degree to which the production plans meet the system's operational support requirements. |
| PSD | Product Specification Document | A document that provides the technical specifications relating to the formatting and content of a particular data product. |
| RQMT | Requirements Documents | RDs are detailed requirements allocated from the project to the next lower level of the project. |
| SAR | System Acceptance Reviews | SARs evaluate whether a specific end item is sufficiently mature to be shipped from the supplier to its designated operational facility or launch site. |
| SDMP | Science Data Management Plan | The SDMP describes how the program will manage the scientific data generated and captured by the operational mission(s). The SDMP also includes descriptions of how data will be generated, processed, distributed, analyzed, and archived. |
| SDR | System Definition Reviews | SDRs evaluate the credibility and responsiveness of the proposed program requirements/architecture to the Mission Directorate requirements and constraints, including available resources, and allocation of requirements to projects. SDRs also determine whether the maturity of the program's mission/system definition and associated plans are sufficient to begin preliminary design. |
| SIR | System Integration Reviews | SIRs evaluate the readiness of the program, including its projects and supporting infrastructure, to begin system AI&T with acceptable risk and within cost and schedule constraints. |
| SMSR | Safety and Mission Success Reviews | SMSRs prepare Agency safety and engineering management to participate in program final readiness reviews preceding flights or launches, including experimental/test launch vehicles or other reviews as determined by the Chief, Safety and Mission Assurance. SMSRs also provide the knowledge, visibility, and understanding necessary for senior safety and engineering management to either concur or nonconcur in program decisions to proceed with a launch or significant flight activity. |
| SRB | Standing Review Board | The SRB is responsible for conducting independent reviews (life cycle and special) of a program/project and providing objective, expert judgments to the convening authorities. The reviews are conducted in accordance with approved Terms of Reference (ToR) and life-cycle requirements per this document and NPR 7123.1. |
| SRR | System Requirements Reviews | SRRs evaluate whether the functional and performance requirements defined for the system are responsive to the Mission Directorate requirements on the program and its projects and represent achievable capabilities. |