MODIS Filenames
MODIS filenames (i.e., the local granule ID) follow a naming convention which gives useful information regarding the specific product. Product short name designations are as follows: MOD for Terra MODIS, MYD for Aqua MODIS, and MCD for Terra and Aqua combined MODIS.
In this example of a swath product, the filename MOD14.A2023082.0430.061.2023082091705.hdf indicates:
- MOD14 - Product Short Name
- A2023082 - Julian Date of Acquisition (AYYYYDDD)
- 0430 - Hours and Minutes of Acquisition (HHMM)
- 061 - Collection Version
- 2023082091705 - Julian Date of Production (YYYYDDDHHMMSS)
- .hdf - Data Format (HDF-EOS)
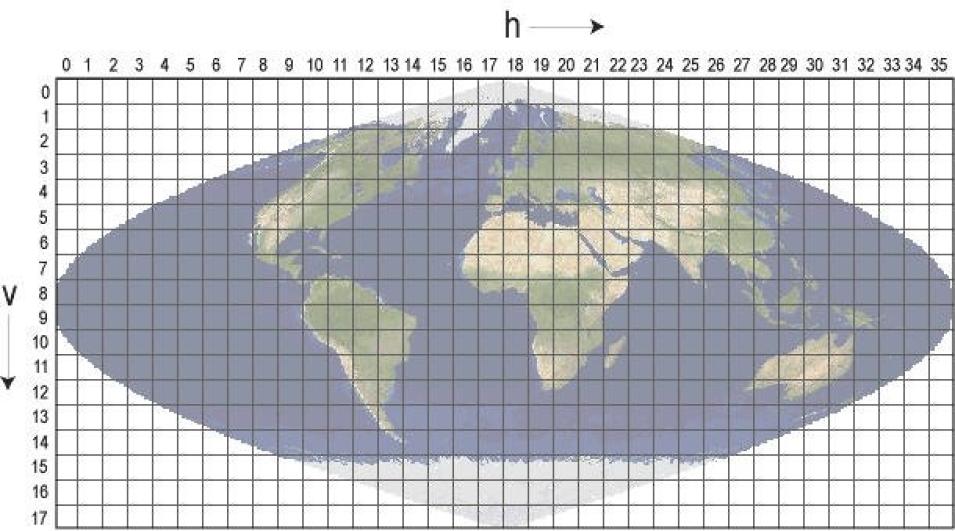
In this example of a tiled product, the filename MCD19A2.A2023081.h22v02.061.2023082164002.hdf indicates:
- MCD19A2 - Product Short Name
- A2023081 - Julian Date of Acquisition (AYYYYDDD)
- h22v02 - Tile Identifier (horizontalXXverticalYY)
- 061 - Collection Version
- 2023082164002 - Julian Date of Production (YYYYDDDHHMMSS)
- .hdf - Data Format (HDF-EOS)
In this example for a Climate Modeling Grid (CMG) product, the filename MYD09CMG.A2023081.061.2023083032243.hdf indicates:
- MYD09CMG - Product Short Name
- A2023081 - Julian Date of Acquisition (AYYYYDDD)
- 061 - Collection Version
- 2023083032243 - Julian Date of Production (YYYYDDDHHMMSS)
- .hdf - Data Format (HDF-EOS)
MODIS Product Long Name
The MODIS Product Long Name (i.e., Collection-Level) naming convention provides useful information regarding the product and indicates if the associated files for the dataset are swath, Sinusoidal tile grid, or CMG. Swath products are produced in 5-minute temporal increments of satellite acquisition.
In this example for a swath dataset, all products belonging to the MODIS/Terra Thermal Anomalies/Fire 5-Minute L2 Swath 1 km V061 collection have the following characteristics:
- MODIS/Terra - Instrument/Satellite
- Thermal Anomalies/Fire - Geophysical Parameter
- 5-Minute - Temporal Resolution
- L2 - Processing Level
- Swath - Swath
- 1 km - Spatial Resolution
- V061 - Collection Version
In this example for a tiled dataset, all products belonging to the MODIS/Terra+Aqua Land Aerosol Optical Depth Daily L2G Global 1 km SIN Grid V061 collection have the following characteristics:
- MODIS/Terra+Aqua - Instrument/Satellite
- Land Aerosol Optical Depth - Geophysical Parameter
- Daily - Temporal Resolution
- L2G - Processing Level
- Global - Global Coverage
- 1 km – Spatial Resolution
- SIN Grid - Sinusoidal Grid
- V061 - Collection Version
In this example for a CMG dataset, all products belonging to the MODIS/Aqua Surface Reflectance Daily L3 Global 0.05 Deg CMG V061 collection have the following characteristics:
- MODIS/Aqua - Instrument/Satellite
- Surface Reflectance - Geophysical Parameter
- Daily - Temporal Resolution
- L3 - Processing Level
- Global - Global Coverage
- 0.05 Deg - Spatial Resolution
- CMG - Climate Modeling Grid
- V061 - Collection Version