NASA has announced that all RADARSAT-1 data archived at the Alaska Satellite Facility Distributed Active Archive Center (ASF DAAC) are now open data and can be freely downloaded.
Anyone who has registered with NASA Earthdata Login and agreed to the ASF End User License Agreement can now download RADARSAT-1 data from the ASF DAAC.
The Canadian Space Agency’s (CSA) RADARSAT-1 satellite was launched in 1995 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Ground support for the mission was provided by NASA through its ASF and McMurdo, Antarctica, tracking facilities. Through an agreement between CSA and the U.S. government, synthetic aperture radar data (SAR) acquired by RADARSAT-1 and downlinked at the NASA ground stations were processed and archived at ASF DAAC. The satellite mission ended in 2013.
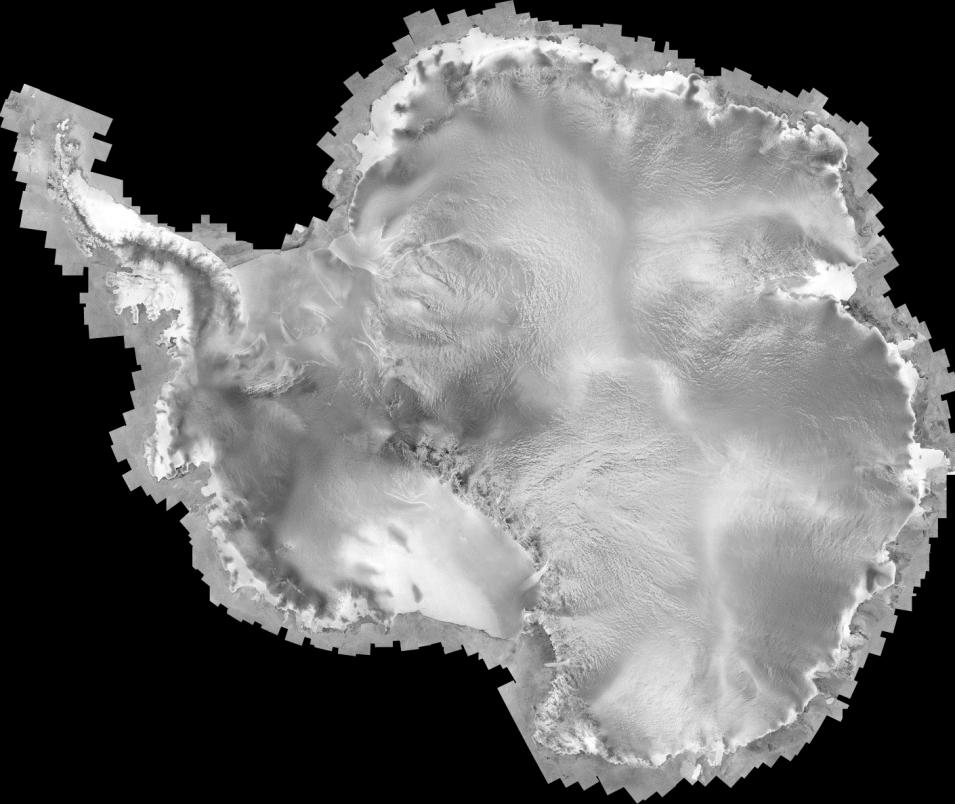
Protecting the environment and monitoring global change is a priority of the Canadian space program, and RADARSAT-1 was the flagship satellite of this effort. Because of its wide range of operational modes and frequency of repeat observations, RADARSAT-1 proved invaluable for monitoring sea ice and terrestrial ice sheets, climate research, identifying and mapping land features, and assessing environmental change over time. Data from the satellite were used to compile the first complete, high-resolution map of Antarctica. (Mosaics from this dataset are available to download from ASF DAAC.)
CSA and NASA have cooperated since the beginning of the satellite mission to distribute processed SAR data through ASF, primarily to U.S. Earth science researchers. The recent agreement between CSA and NASA now makes these data freely and openly available to the global research community.
Contact uso@asf.alaska.edu for more information.