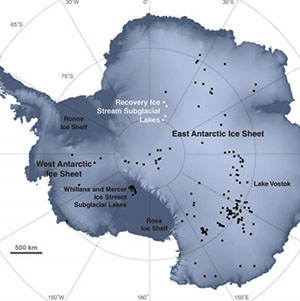
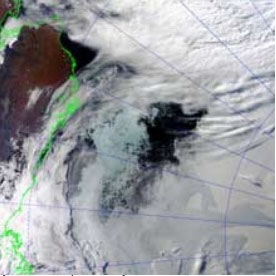
Synthetic aperture radar, or SAR, uses the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. SAR can penetrate cloud cover and “see through” darkness and weather, allowing a unique view of flood inundation, land cover changes, and modifications of Earth’s surface from landslides, earthquakes, and background tectonic motion. NASA’s home for SAR data and imagery is the Alaska Satellite Facility Distributed Active Archive Center (ASF DAAC).