Copyright © 2017 The HDF Group
This example code illustrates how to access and visualize NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center (NSIDC DAAC) Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR) Hierarchical Data Format - Earth Observing System 5 (HDF-EOS5) Point product in Python via OPeNDAP.
If you have any questions, suggestions, or comments on this example, please use the HDF-EOS Forum (http://hdfeos.org/forums).
If you would like to see an example of any other NASA HDF/HDF-EOS data product that is not listed in the HDF-EOS Comprehensive Examples page (http://hdfeos.org/zoo), feel free to contact us at eoshelp@hdfgroup.org or post it at the HDF-EOS Forum.
Tested under: Python 2.7.13 :: Anaconda 4.3.1 (x86_64)
import os import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap import numpy as np import csv import urllib2 import math
Set OPeNDAP URL. NSIDC runs a Hyrax server that enables CF output for HDF5 data product. Such server cannot handle compound data type in HDF-EOS5 Point data product. Therefore, we copied a sample file and put it on our demo Hyrax server that disabled CF Output.
For large subset of data, this code will not work for some reason. Thus, we select 10 points using OPeNDAP's constraint expression.
Neither PyDAP nor netCDF4 python module can handle OPeNDAP's array of structure.Thus, we will read data in ASCII instead of DAP2.
url = ("https://eosdap.hdfgroup.org:8989" # Server
"/opendap/hyrax/data/NASAFILES/hdf5/" # Path to data on server
"AMSR_U2_L2_Land_B01_201207232336_D.he5" # HDF-EOS5 Point file
".ascii?" # OPeNDAP request
"/HDFEOS/POINTS/AMSR-2%20Level%202%20Land%20Data/Data/" # Group Path
"Combined%20NPD%20and%20SCA%20Output%20Fields" # HDF5 Dataset
"[3700:1:3709]") # OPeNDAP constraint - select 10 points.
response = urllib2.urlopen(url)
cr = csv.reader(response)
# The first line of output is dataset name.
i = 0
# Every 3rd row is the actual value in CSV format.
j = -1
lat = np.array([], dtype=float)
lon = np.array([], dtype=float)
data = np.array([], dtype=float)
for row in cr:
if i != 0:
j = j+1
if i != 0 and (j % 3 == 2):
# Latitude
# print row[1]
lat = np.append(lat, float(row[1]))
# Longitude
# print row[2]
lon = np.append(lon, float(row[2]))
# SoilMoistureNPD
# print row[16]
data = np.append(data, float(row[16]))
i = i+1
print lat, lon, data
[-5.95511 -6.1588 -6.35505 -6.56324 -6.75285 -6.96071 -7.14491 -7.34555 -7.53102 -7.7309 ] [ 17.9583 17.9724 17.9519 17.9644 17.9538 17.9567 17.9625 17.952 17.9661 17.9547] [ 0.13084 0.122343 0.130008 0.140189 0.148062 0.155974 0.153412 0.144981 0.147109 0.150234]
Let's plot the data using the above lat/lon/data ASCII values retrieved from OPeNDAP server.
m = Basemap(projection='cyl', resolution='l',
llcrnrlat=-90, urcrnrlat=90,
llcrnrlon=-180, urcrnrlon=180)
m.drawcoastlines(linewidth=0.5)
m.scatter(lon, lat, c=data, s=1, cmap=plt.cm.jet, edgecolors=None, linewidth=0)
fig = plt.gcf()
plt.show()
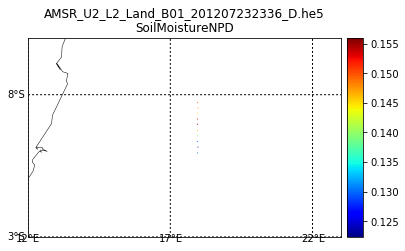
It's hard to see the data on global map. Let's zoom in.
m = Basemap(projection='cyl', resolution='l',
llcrnrlat=math.floor(np.min(lat))+5,
urcrnrlat=math.ceil(np.max(lat))-5,
llcrnrlon=math.floor(np.min(lon)-5),
urcrnrlon=math.ceil(np.max(lon))+5)
m.drawcoastlines(linewidth=0.5)
m.drawparallels(np.arange(math.floor(np.min(lat))-5,
math.ceil(np.max(lat))+5, 5),
labels=[True,False,False,False])
m.drawmeridians(np.arange(math.floor(np.min(lon))-5,
math.ceil(np.max(lon))+5, 5),
labels=[False,False,False,True])
m.scatter(lon, lat, c=data, s=1, cmap=plt.cm.jet, edgecolors=None, linewidth=0)
cb = m.colorbar()
basename = 'AMSR_U2_L2_Land_B01_201207232336_D.he5'
plt.title('{0}\n{1}'.format(basename, 'SoilMoistureNPD'))
fig = plt.gcf()
plt.show()
You can save it as CSV and visualize data easily with Excel.
a = np.column_stack((lat, lon, data))
print a
np.savetxt("AMSR_U2_L2.csv", a, delimiter=",")
[[ -5.95511 17.9583 0.13084 ] [ -6.1588 17.9724 0.122343] [ -6.35505 17.9519 0.130008] [ -6.56324 17.9644 0.140189] [ -6.75285 17.9538 0.148062] [ -6.96071 17.9567 0.155974] [ -7.14491 17.9625 0.153412] [ -7.34555 17.952 0.144981] [ -7.53102 17.9661 0.147109] [ -7.7309 17.9547 0.150234]]
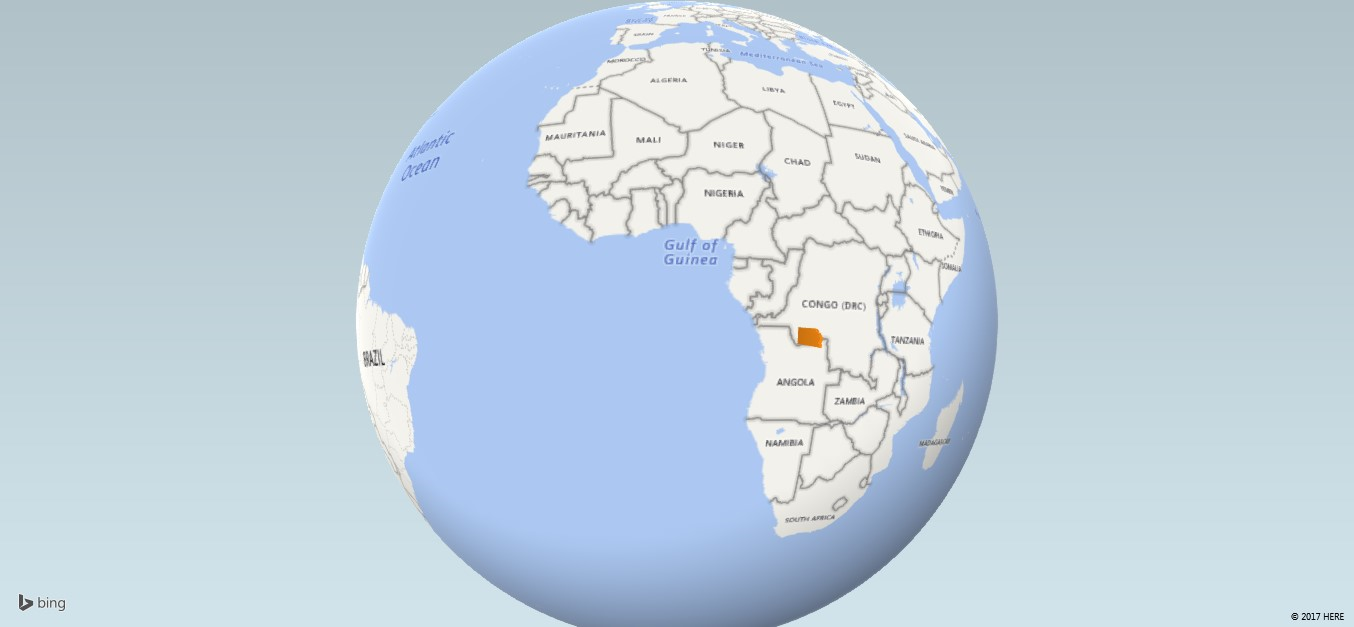
Here's the Excel 3-D Map image generated from the above CSV file.